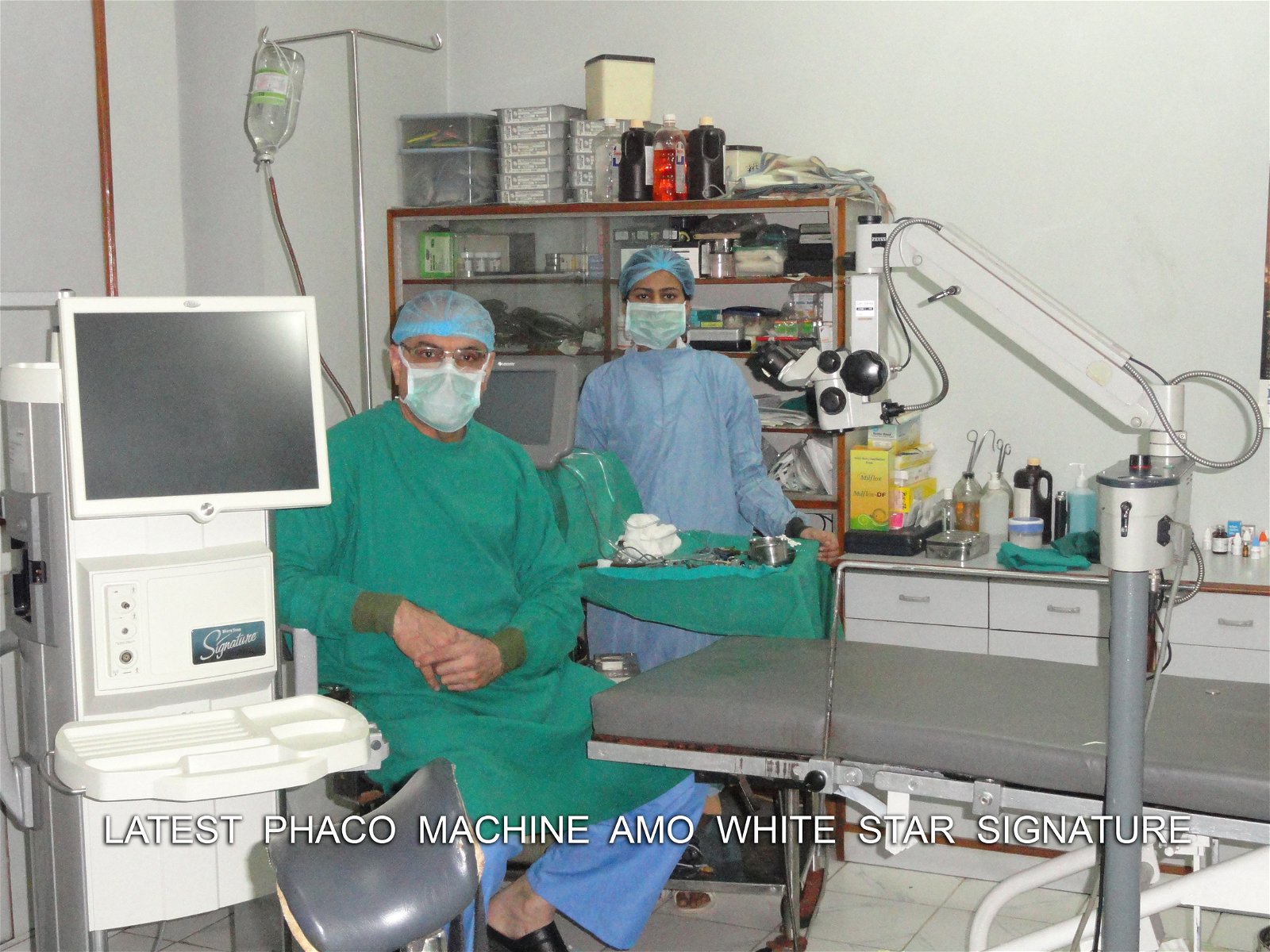
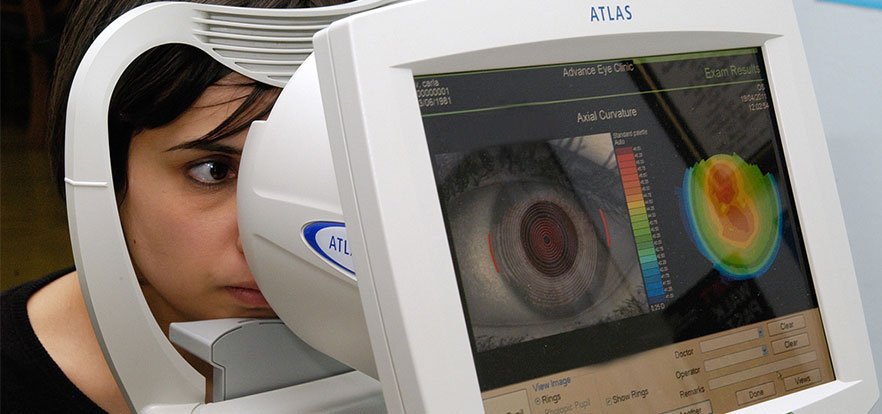
What is a cataract?
A cataract is a painless, cloudy area in the lens of the eye that blocks the passage of light to the retina. The retina is the nerve layer at the back of the eye. The nerve cells in the retina detect light entering the eye and send nerve signals to the brain about what the eye sees. Because cataracts block this light, they can cause vision problems.
Causes of cataract:-
Aging (age-related cataracts) called senile cataract,the most common,which can be immature,mature,hypermature depending on the stage patient present to the eye surgeon..
- Overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, such as from sunlight, tanning booths, or sunlamps.
- Diabetes. Diabetes, especially when the blood sugar levels are above the safe range, causes changes in the eye that can result in cataracts.
- Disease inside the eye, such as glaucoma, retinitis pigmentosa, retinal detachment, or long-term uveitis.
- Long-term use of steroid medicines.
- Frequent X-rays or radiation treatments to the head.
- Family history (genetics). A person may inherit the tendency to develop cataracts.
- Vitrectomy. People older than age 50 who have had the vitreous gel removed from their eye (vitrectomy) have an increased risk of cataracts.
- Eye injury. Even though injury-related cataracts are rare, injury is a leading cause of cataracts in children.
- Being born with cataracts (congenital). Some children are born with the condition.
Symptom of cataract:-
- You may have cloudy, fuzzy, or foggy vision.
- You may see glare from lamps or the sun. You may have trouble driving at night because of glare from car headlights.
- You may need frequent changes to your eyeglasses prescription.
- You may get double vision in one eye.
- Your near vision may improve for a short time if you get a cataract. This temporary improvement is called second sight.
- The vision loss from a cataract often happens slowly and may never become severe.
How are cataracts diagnosed?
Your doctor can find out if you have cataracts by doing a physical exam and by asking questions about your symptoms and past health. You may need tests to make sure you have a cataract or to rule out other conditions that may be causing vision problems.
How are they treated?
Surgery only can remove cataracts. For most adults, surgery is only needed when vision loss caused by a cataract affects their quality of life,daily activity like driving,reading,and other activity involved in professional/business activity
As a cataract progresses, more of the lens becomes cloudy. When the entire lens is white, the cataract is called a "ripe" or "mature" cataract and causes severe vision problems. Delaying surgery until cataracts are ripe or mature is neither recommended nor needed.
Cataracts - Exams and Tests
Diagnosis of cataracts is based on a medical history and physical exam.
Cataracts - Treatment Overview
Surgery is the only effective method of treating vision loss caused by cataracts.
Cataract surgery is a common procedure that involves removing the clouded lens of the eye (the cataract). The lens can be replaced with an artificial lens called an intraocular lens implant (IOL),
After cataract surgery
Your doctor will give you instructions about what to do after cataract surgery. Eye care for adults after cataract surgery includes using prescribed eyedrops, protecting your eye, and watching for signs of infection.
Contact your doctor promptly if you notice any signs of complications, such as:
- Decreasing vision.
- Increasing pain.
- Increasing redness.
- Swelling around the eye.
- Any discharge from the eye.
- Any new floaters, flashes of light, or changes in your field of vision.
- Intraocular lens (IOL) . A variety of IOL types are available. Work with your doctor to choose the best one for you.
- Improving vision,both for near and distance,with multifocal iols.
- Helping you return to work, leisure, and other daily activities.
Surgery Choices
There are two types of cataract surgery. They are both done in an outpatient center. The decision about which one to use depends on what kind of cataract you have and how much experience the surgeon has with each type of surgery.
- Phacoemulsification (small-incision surgery). In this type of surgery, the incisions are small, and sound waves (ultrasound) are used to break up the lens into small pieces. This is the most common method of doing cataract surgery.
- Standard extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE). In this type of surgery, the lens and the front portion of the lens capsule wrapped around the lens is opened. The lens is then carefully removed in one piece
If you do not have another eye condition, such as glaucoma or problems with your retina, your chances of seeing better after cataract surgery are very good. But you may still need reading glasses or glasses for near vision.Multifocal IOLS can be implanted to reduce the dependence on glasses for near and distance vision.
Refractive errors (eye sight defects)
Nearsightedness (myopia)
Nearsightedness -- or myopia -- affects a significant number of people. But this eye disorder is easily corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or lasik surgery.
People with myopia or nearsightedness have difficulty seeing distant objects, but can clearly see objects that are near.
What Causes Nearsightedness?
People who are nearsighted have what is called a refractive error. In nearsighted people, the eyeball is too long or the cornea has too much curvature, so the light entering the eye is not focused correctly. Images focus in front of the retina, the light-sensitive part of the eye, rather than directly on the retina, causing blurred vision.
Nearsightedness runs in families and usually appears in childhood. Usually the condition plateaus, but it can worsen with age.
What Are the Symptoms of Nearsightedness?
People who are nearsighted often complain of headaches, eyestrain, squinting, or fatigue when driving, playing sports, or looking more than a few feet away. Children commonly complain of not being able to see the board at school.
How Is Nearsightedness Diagnosed?
Nearsightedness can be easily diagnosed using standard eye exams given by an eye doctor.
How Is Nearsightedness Treated?
Glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery can correct nearsightedness. Refractive surgery can reduce or even eliminate your dependence on glasses or contact lenses. The most common procedures for nearsightedness include:
- Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis. This surgery is commonly called LASIK. The surgeon uses a laser to cut a flap through the top of the cornea. Then a laser removes some corneal tissue, and the flap is dropped back into place. LASIK is the most common surgery used to correct nearsightedness.
- Farsightedness (hyperopia)Farsightedness or hyperopia means that the eye focuses better on distant objects than on those that are close.
Symptoms of farsightedness may include:
- Headaches
- Eye strain
- Difficulty concentrating or focusing on nearby objects
- Fatigue or headache after performing a close task such as reading Glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery can all be used to correct farsightedness.
- LASIK is the most common surgery used to correct farsightedness.
Talk to your eye doctor about which treatment is best for you.